मनुष्य would not have existed without वायरस because viral protein plays a key role in the development of मानव embryo. However, at times, they pose existential threats in the form of diseases as in the case of current COVID-19 pandemic. Ironically, वायरस comprise ~8% of our genome, that has been acquired during the course of evolution, making us “virtually a chimera”.
बिना शक साल 2020 का सबसे बदनाम और खौफनाक शब्द है 'वाइरस'। उपन्यास कोरोना वर्तमान अभूतपूर्व COVID-19 बीमारी और विश्व अर्थव्यवस्था के लगभग पतन के लिए जिम्मेदार है। यह सब एक छोटे से कण के कारण होता है जिसे 'पूरी तरह से' जीवित भी नहीं माना जाता है क्योंकि यह मेजबान के बाहर एक गैर-कार्यात्मक स्थिति में है, जबकि मेजबान को संक्रमित करने पर केवल अंदर ही रहता है। इससे भी अधिक आश्चर्यजनक और चौंकाने वाला तथ्य यह है कि मनुष्य have been carrying the viral “genes” since times immemorial and currently viral genes constitutes ~8% of the मानव genome (1). Just to put this in perspective, only ~1% मानव genome is functionally active responsible for making proteins that determine who we are.
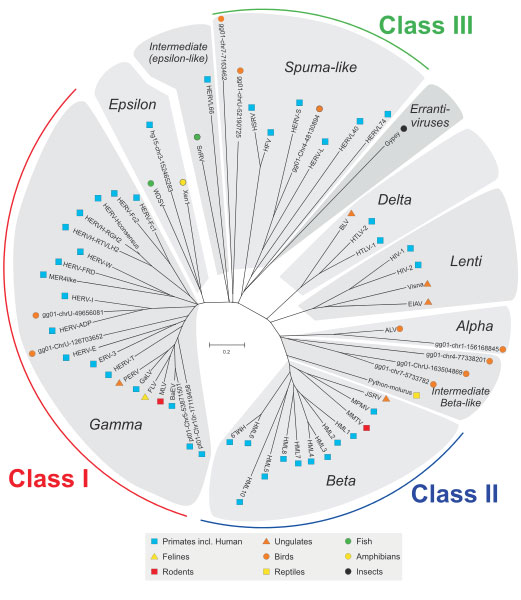
The story of relationship between मनुष्य और वायरस इसकी शुरुआत 20-100 मिलियन वर्ष पहले हुई थी जब हमारे पूर्वज इससे संक्रमित हुए थे वायरस. Each endogenous retrovirus family is derived from a single infection of the germline cells by an exogenous retrovirus that after integrating into our ancestor, expanded and evolved (2). The propagation followed by the horizontal transfer from parents to offspring and today we have these viral genomes embedded in our DNA as मानव endogenous retroviruses (HERVs). This is a continuous process and may even be happening at the moment. Over the course of evolution, these HERVs acquired mutations, became stabilised in the मानव genome and lost their ability to cause the disease. The endogenous रेट्रोवायरस are not only present in मनुष्य but are omnipresent in all living organisms. All these endogenous retroviruses grouped into three classes (Class I, II and III) occurring across different animal species exhibit a phylogenetic relationship based on their sequence similarity (3) as depicted in Figure below. HERVs belong to the Class I group.
Of the various embedded retroviruses present in the मानव genome, a classic example worth mentioning here, is that of a retroviral protein that is highly fusogenic envelope protein called syncytin, (5) whose original function in the वाइरस was to fuse with host cells to cause infection. This protein has now been adapted in मनुष्य to form placenta (fusion of cells to make multinucleated cells) that not only provides food to foetus from the mother during pregnancy but also protects the foetus from the mother’s immune system due to the immunosuppressive nature of the syncytin protein. This particular HERV has proven to be beneficial to the मानव race by defining its very existence.
HERVs have also been implicated in providing innate immunity to the host by preventing further infection from related वायरस or reducing the severity of the disease upon re-infection by similar type of वायरस. A 2016 review by Katzourakis and Aswad (6) describes that endogenous वायरस can act as regulatory elements for genes that control immune function, thereby leading to immunity development. In the same year, Chuong et al (7) demonstrated that certain HERVs act as regulatory enhancers by modulating the expression of IFN (interferon) inducible genes thereby providing innate immunity. HERV expression products can also act as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), triggering the cellular receptors responsible for host first line of defences (8-10).
एचईआरवी का एक और दिलचस्प पहलू यह है कि उनमें से कुछ सम्मिलन बहुरूपता दिखाते हैं, अर्थात सम्मिलन की घटनाओं के कारण जीनोम में अलग-अलग संख्या में प्रतियां मौजूद हैं। विभिन्न जातीय समूहों से संबंधित 20 विषयों के एक अध्ययन में सभी विषयों (0) में 87-11% के बीच सम्मिलन बहुरूपता पैटर्न का पता चला। इसके कुछ जीनों के सक्रिय होने से रोग पैदा करने में निहितार्थ हो सकते हैं जो अन्यथा चुप हैं।
कुछ एचईआरवी को भी मल्टीपल स्केलेरोसिस (12) जैसे ऑटोइम्यून विकारों के विकास से जुड़ा हुआ दिखाया गया है। सामान्य शारीरिक स्थितियों के तहत, HERV अभिव्यक्ति को कसकर नियंत्रित किया जाता है, जबकि बाहरी / आंतरिक वातावरण में परिवर्तन के कारण पैथोलॉजिकल परिस्थितियों में, हार्मोनल परिवर्तन और / या माइक्रोबियल इंटरैक्शन के कारण HERV अभिव्यक्ति की विकृति हो सकती है, जिससे बीमारी हो सकती है।
The above characteristics of HERVs suggest that not only their presence in मानव genome is inevitable but they possess the ability to regulate the homeostasis of the immune system either by activating or suppressing it, thereby causing differential effects (from being beneficial to causing a disease) in hosts.
COVID-19 महामारी भी एक रेट्रोवायरस SARS-nCoV-2 के कारण होती है, जो इन्फ्लूएंजा परिवार से संबंधित है, और यह प्रशंसनीय हो सकता है कि, विकास के दौरान, इस परिवार से संबंधित जीनोम वायरस got integrated into the मानव genome and are now present as HERVs. It is surmised that these HERVs might exhibit different polymorphisms, as mentioned above, among people of different ethnicity. These polymorphisms may be in the form of differential copy number of these HERVs and/or presence or absence of mutations (changes in the genome sequence) accumulated over a period of time. This variability in the integrated HERVs may offer an explanation for the differential mortality rates and the severity of COVID-19 disease in different countries effected by the pandemic.
***
सन्दर्भ:
1. Griffiths DJ 2001. Endogenous retroviruses in the मानव genome sequence. Genome Biol. (2001); 2(6) Reviews 1017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2001-2-6-reviews1017
2. बोके, जेडी; स्टोय, जेपी (1997)। "रेट्रोट्रांस्पोन्सन, अंतर्जात रेट्रोवायरस, और रेट्रोएलेमेंट्स का विकास"। ताबूत में, जेएम; ह्यूजेस, एसएच; वर्मस, एचई (संस्करण)। रेट्रोवायरस। कोल्ड स्प्रिंग हार्ब लेबोरेट्री प्रेस। पीएमआईडी 21433351।
3. Vargiu L, et al. Classification and characterization of मानव endogenous retroviruses; mosaic forms are common. Retrovirology (2016); 13: 7. DOI: 10.1186 / s12977-015-0232-y
4. Classes_of_ERVs.jpg: जर्न पी, स्परबर जीओ, ब्लोमबर्ग जे (डेरिवेटिव वर्क: एफग्राममेन (टॉक)), 2010। ऑनलाइन उपलब्ध https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Classes_of_ERVs.svg 07 मई 2020 को एक्सेस किया गया
5. Blond, JL; Lavillette, D; Cheynet, V; Bouton, O; Oriol, G; Chapel-Fernandes, S; Mandrandes, S; Mallet, F; Cosset, FL (7 April 2000). “An envelope glycoprotein of the मानव अंतर्जात retrovirus एचईआरवी-डब्ल्यू मानव प्लेसेंटा और फ़्यूज़ कोशिकाओं में व्यक्त होता है जो टाइप डी स्तनधारी रेट्रोवायरस रिसेप्टर को व्यक्त करता है। जे. विरोल. 74 (7): 3321-9. डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.74.7.3321-3329.2000.
6. काट्ज़ौराकिस ए, और असवाद ए. विकास: अंतर्जात वायरस एंटीवायरल इम्यूनिटी में शॉर्टकट प्रदान करें। वर्तमान जीवविज्ञान (2016)। 26: आर427-आर429। http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.072
7. चुओंग ईबी, एल्डे एनसी, और फेसचोटे सी। अंतर्जात रेट्रोवायरस के सह-विकल्प के माध्यम से जन्मजात प्रतिरक्षा का नियामक विकास। विज्ञान (2016) वॉल्यूम। 351, अंक 6277, पीपी। 1083-1087। डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad5497
8. वोल्फ एफ, लीश एम, ग्रील आर, रिस्क ए, प्लीयर एल। हाइपोमेथिलेटिंग एजेंटों द्वारा जीन की (पुनः) अभिव्यक्ति की दोधारी तलवार: लक्षित प्रतिरक्षा चेकपॉइंट मॉड्यूलेशन के लिए प्राइमिंग एजेंटों के रूप में वायरल मिमिक्री से शोषण तक। सेल कम्युन सिग्नल (2017) 15:13। डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-017-0168-z
9. हर्स्ट टीपी, मैगियोर्किनिस जी। अंतर्जात द्वारा जन्मजात प्रतिरक्षा प्रतिक्रिया का सक्रियण रेट्रोवायरस. जे जनरल विरोल. (2015) 96:1207-1218। डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.000017
10. चियापिनेली केबी, स्ट्रिसेल पीएल, डेसरीचार्ड ए, चैन टीए, बायलिन एसबी, कॉरेस्पोंडेंस एस। डीएनए मिथाइलेशन को रोकना अंतर्जात रेट्रोवायरस सहित डीएसआरएनए के माध्यम से कैंसर में एक इंटरफेरॉन प्रतिक्रिया का कारण बनता है। सेल (2015) 162:974–986। डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.011
11. मेहराब जी, सिबेल वाई, कनिये एस, सेवगी एम और नर्मिन जी। मानव अंतर्जात retrovirus-एच प्रविष्टि स्क्रीनिंग। आणविक चिकित्सा रिपोर्ट (2013)। डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1295
12. ग्रोगर वी, और सिनिस एच। मानव अंतर्जात रेट्रोवायरस और मल्टीपल स्केलेरोसिस जैसे ऑटोइम्यून विकारों के विकास में उनकी भूमिका। फ्रंट माइक्रोबायल। (2018); 9: 265. डीओआई: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00265
***